Audiology
Best Hearing Aid Services in Hyderabad
Hearing Aid Solutions in Hyderabad
Hearing Aid Dealers
As per a recent census report 1 in 10 people in our country suffer from a hearing loss, the number is staggeringly high and there is a need to conduct a thorough hearing evaluation for all. Unlike eye sight, hearing problem is often detected much later and even when detected people tend to ignore it till it becomes severe.
We hear over different frequency ranges i.e. from 20hertz to 20000 hertz and the normal limits of hearing expressed in terms of decibels is placed at 25 as per Indian standards. If someone is not able to hear sounds at different frequency levels up to the level of 25 decibels, then the individual is said to have a hearing loss. As normal speech conversation level is at 40-50 decibel, an individual with a mild loss is easily able to ignore his problem when it is at the moderate stage. Furthering the damage, the prevalent social stigma about hearing problems & hearing aids prevent the individual from getting his problem treated or even checked.
Before understanding any pathology associated to hearing, one must fully understand the anatomy and working of it. Let us therefore first understand how the process of hearing works:
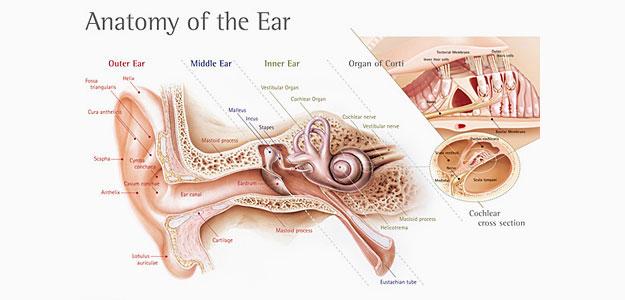
Outer Ear
The function of Outer Ear is to act as a funnel for sound waves from the environment thereby concentrating / funneling them from a relatively larger area i.e. the atmosphere into the ear canal. These waves then pass through the Tympanic Membrane or the ear drum making it to oscillate back & forth thereby passing the energy to the middle ear.
Middle Ear
Middle Ear is where we have three bones namely “Malleus”, Incus & Stapes. These bones are attached to the tympanic membrane on the outer side and inner ear on the other. Once the sound energy passes though the tympanic membrane, it gets converted to mechanical energy in the middle ear thereby making the bones to vibrate. Through this vibration, the mechanical energy gets passed on the Inner Ear.
Inner Ear
The Inner Ear contains “Cochlea” which is studded with hair cells and contains a thick viscous fluid. It is here that the mechanical energy gets converted to electro-magnetic impulses through the motion of the fluid. The cochlea is attached to the auditory nerve which has a function to carry these electro-magnetic nerve impulses to the brain where we understand this energy as sound.
A hearing loss may have several orientations, and these are classified under three broad categories namely:
1. Conductive
2. Sensorineural
3. Mixed
In simple terms, a conductive hearing loss occurs when the outer and/or middle ear is affected. There can be several reasons for this type of loss including any kind of injury, birth defects, infections in the ear, diseases such as otosclerosis etc
Anything that results in the blockage of the ear canal or the acoustic path can affect the outer ear functions resulting in a conductive loss. This may include an under developed Pinna which is a congenital disorder, or excessive accumulation of cerumen or the ear wax which blocks the passage of acoustic energy travelling through the canal.
Problems which constitute to hindering the healthy functions of the middle ear are:
- Middle Ear Infections
- Otosclerosis
- Tumors
- Congenital Defects
- Medicinal side effects (generally antibiotics)
Together one or more of the above defects together cause conductive hearing loss in patients. A Sensorineural hearing loss when the vestibulochochlear nerve (which connects the inner ear to the brain) or the central processing centres of the brain are affected. This type of loss can be associated to genetic causes, injuries, side effect of medicines or even the gradual ageing process.
The causes of sensorineural hearing loss may be acquired as well as congenital.
Acquired causes may include :
- Illness or Diseases (Meningitis, Viral, Measles, Mumps, Syphilis)
- Antibiotics/ Medicines (Ototoxic Drugs)
- Long term exposure to noise
- Physical Trauma/ Injury etc
Congenital reasons may include an :
- Underdeveloped Cochlea
- Poor hair cell functions
- Chromosomal syndromes
- Rh Incompatibility (in pregnant women)
A Mixed loss is a combination of both sensorineural and conductive components. This means that in a mixed loss, the patient may be suffering from problems in outer, middle as well as the inner ear. The loss can range from mild to profound categories.
This self-check is an easy-at-home screening that will help you judge whether you have a hearing loss or not.
Although this is certain that this screening check is not a substitute to a detailed assessment done by a hearing professional i.e. an audiologist or an ENT Doctor.
This will only help you think into some of the day to day activities and determine whether you face any difficulty there
Hear Better Live Better.
Stay Connected
Smart Solutions for Smarter Hearing
Call Now

